2007- 2008 Using Electrical Resistivity Imaging to Evaluate Permanganate Performance during an In Situ Treatment of a RDX-Contaminated Aquifer
Vitaly Zlotnik's research | Go back to his website
Funded by ESCTP joint program of Department of Defense and Environmental Protection Agency
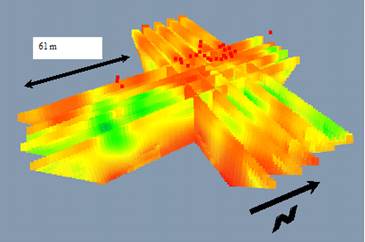
Assessment of groundwater remediation efforts typically involves discrete point sampling using wells, multilevel piezometers, or direct push. These methods, however, can miss contaminants when flow paths do not conform to the predetermined sampling grids. Our study at the Nebraska Ordnance Plant Superfund site at Mead, Nebraska supplements permanganate injection. It uses electrical resistivity (ER) imaging as an alternative to point sampling for a more complete delineation of contaminant plumes, when ER of oxidant differs from ER of ambient flow. The multi-electrode array introduces current into the ground and measures the potential field. An inversion algorithm produces 2D or 3D spatial plume distributions. Our published results describe the effectiveness of targeting the localized conductive zones in the sand and gravel aquifer of Todd Valley.
Publications
Halihan, T., J. Albano, S.D. Comfort, V.A. Zlotnik, 2011, Electrical resisitivity imaging of a permanganate injection during in Situ treatment of RDX-contaminated ground water, Ground Water Monitoring & Remediation, published online: 16 AUG 2011, DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-6592.2011.01361.x
Albano, J., Comfort, S. D., Zlotnik, V., Halihan, T., Burbach, M., Chokejaroenrat, C., Onanong, S. and Clayton, W., 2010, In Situ Chemical Oxidation of RDX-Contaminated Groundwater with Permanganate at the Nebraska Ordnance Plant. Ground Water Monitoring & Remediation, 30: 96-106. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6592.2010.01295.x
Standard ERI System

Laying out electrode lines

3D Interpretation of Injected Plume
Verifying Interpretation of Geoprobe Sampling
